Explore the chapters:
Paid advertising has changed significantly over time. Gone are the days when a small investment and basic keyword targeting could yield substantial results. Nowadays, competition is fierce, and every dollar spent needs to be carefully allocated, especially when budgets are tight.
This situation is common across various scenarios. For startups, limited budgets often coincide with the process of finding the right fit for their product in the market. Even for more established businesses, venturing into paid advertising with a small budget for testing is a common scenario. Moreover, economic challenges or shifts in company priorities may lead to reductions in paid advertising budgets.
Given these constraints, it’s crucial to approach budget allocation with caution. Every dollar needs to be used wisely to maximize its impact and generate meaningful returns on investment. This might involve conducting thorough testing, focusing on high-value opportunities, and refining campaigns based on insights gathered from data analysis.
Ultimately, success in paid advertising when budgets are tight requires strategic planning, resourcefulness, and adaptability to changing market conditions. It’s about making the most of available resources to drive tangible outcomes and support business growth in a competitive environment.

Paid advertising is a marketing approach where brands invest to display ads to their intended audiences. While this term can encompass traditional mediums like TV or radio, it’s predominantly associated with online platforms.
Paid advertisements involve advertisers competing for ad space on platforms such as Google Ads or Meta ads. The platforms employ algorithms to determine which ads are displayed and when based on auctions.
Each platform utilizes its own bidding algorithm, typically considering factors like bid amount, ad quality, and user engagement to select ads for display. Consequently, even if two advertisers have identical budgets, the one with more relevant and compelling ads tends to receive greater visibility.
Paid advertising serves as a critical component of a comprehensive marketing strategy, enabling businesses to communicate their offerings effectively to their target audience.

Paid ads provide advantages for businesses of all sizes, including:
Paid ads let businesses of all levels to connect with new audiences, regardless of brand recognition, and offer a range of ad options to suit different needs.
Paid ads are categorized based on the ad format and channels they’re displayed in. Let’s cover five main types.
Sure, here are five main types of paid ads categorized based on their format and display channels:
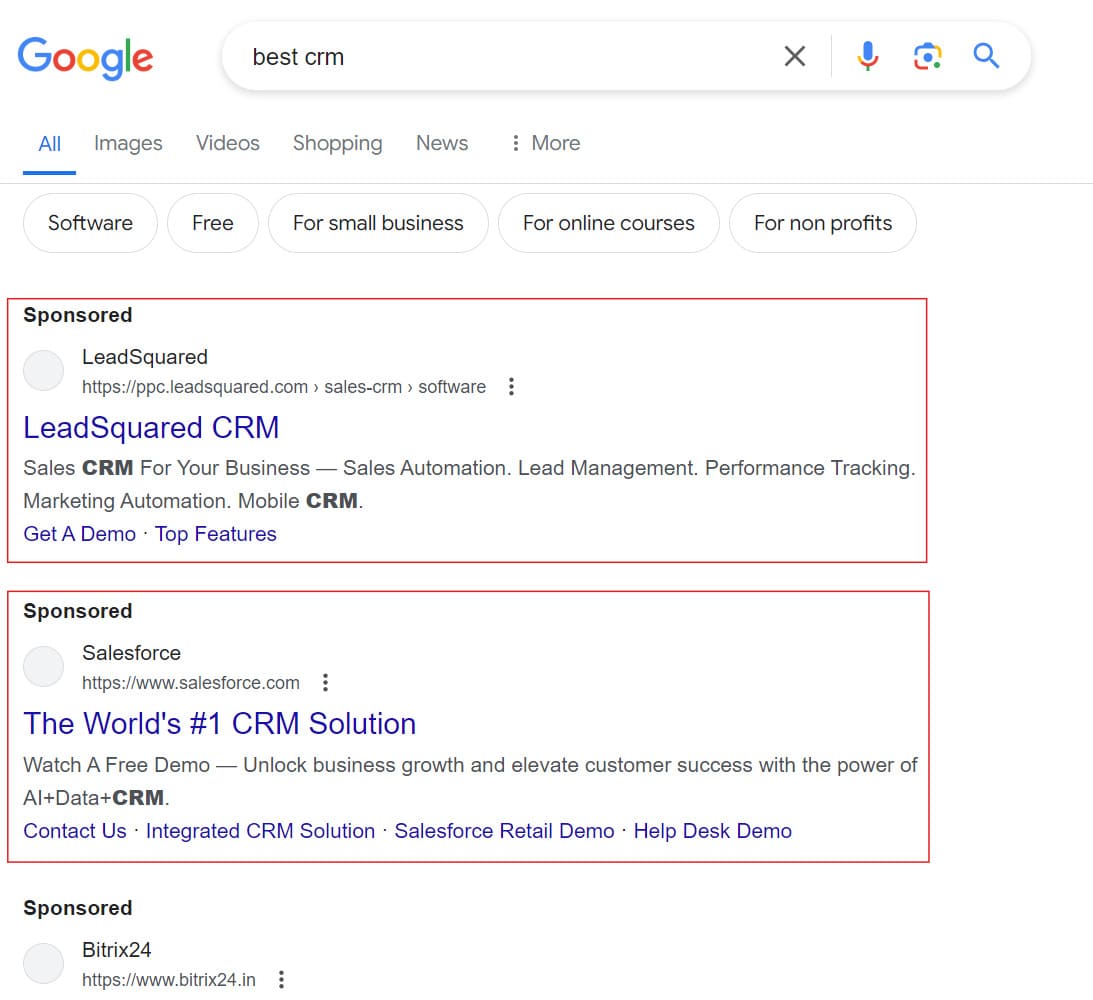
Search ads are a type of online advertising that appear on search engine results pages (SERPs) alongside organic search results. These ads are typically text-based and are triggered by specific keywords or phrases entered by users into the search engine.
When a user searches for a particular term or phrase, relevant search ads are displayed at the top or bottom of the search results page, marked as “sponsored” or “ad.” The placement of these ads is determined by factors such as bid amount, ad quality, and relevance to the user’s search query.
Search ads allow advertisers to target users actively searching for information related to their products or services, making them highly targeted and effective for driving conversions. They often include a headline, a brief description, and a link to the advertiser’s website or landing page, encouraging users to click through to learn more or make a purchase.
Display ads are a form of online advertising that incorporates various visual elements, such as images, videos, or interactive media. These ads are typically displayed on websites within a network of publishers, rather than on search engine results pages.
Unlike search ads, which are triggered by specific search queries, display ads are shown based on targeting criteria set by advertisers, such as demographics, interests, or browsing behaviour. They can appear in different formats and sizes, including banner ads, sidebar ads, interstitial ads, and rich media ads.
Display ads aim to capture users’ attention while they browse the web and drive them to take a specific action, such as visiting a website, signing up for a newsletter, or making a purchase. They often feature compelling visuals and a clear call to action to encourage engagement and conversions.
Social media ads refer to paid advertisements that are displayed on various social media platforms, such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and others. These ads can take different forms and formats, depending on the platform and the advertiser’s objectives.
Common types of social media ads include:
Social media ads offer precise targeting options based on factors such as demographics, interests, behavior, and location, allowing advertisers to reach their desired audience with relevant content. They are a powerful tool for increasing brand awareness, driving website traffic, generating leads, and boosting sales on social media platforms.
Schedule a free consultation call with our team today

Video ads are a form of digital advertising that utilizes video content to promote products, services, or brands. These ads are displayed on various online platforms, including social media, websites, and streaming services, and they can take different formats and lengths.
Common types of video ads include:
Video ads offer advertisers a powerful way to engage audiences with compelling visuals, storytelling, and sound. They are highly effective for increasing brand awareness, driving engagement, and influencing purchase decisions. With the rise of online video consumption, video ads have become an essential component of digital marketing strategies for businesses of all sizes.
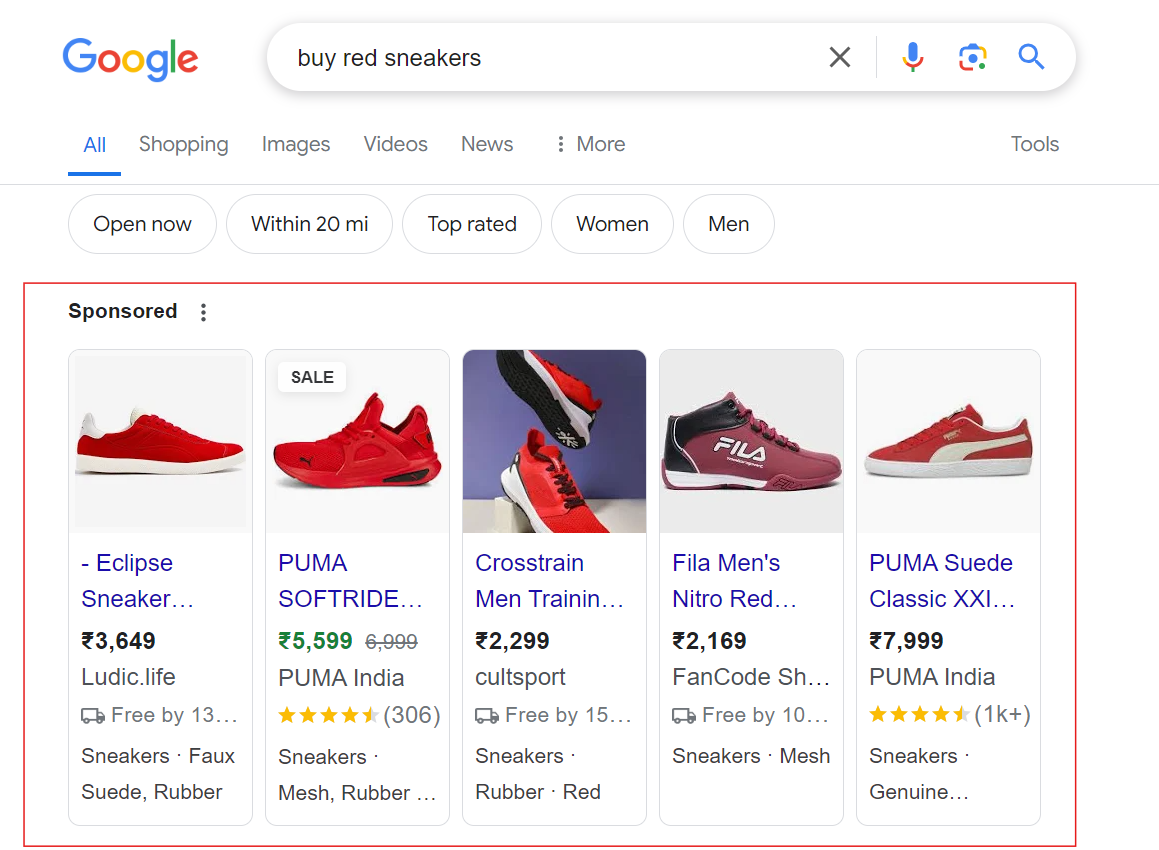
Shopping ads, also known as Product Listing Ads (PLAs), are a type of online advertising specifically tailored for e-commerce businesses. These ads allow retailers to showcase their products directly within search engine results pages (SERPs) and other relevant placements across various platforms.
Key features of shopping ads include:
Shopping ads are triggered by relevant search queries and target users who are actively searching for products or product categories. They are highly effective for increasing product visibility, driving qualified traffic to e-commerce websites, and generating sales and conversions.
By leveraging shopping ads, retailers can effectively showcase their product catalogs, highlight special offers, and reach users with high purchase intent, ultimately maximizing their online sales and revenue.
Native ads are a type of paid advertisement that seamlessly blends in with the content and design of the platform where they are displayed. Unlike traditional banner or display ads, native ads mimic the appearance and format of the surrounding content, making them less disruptive and more engaging to users.
These ads can appear on various digital platforms, including social media feeds, websites, and mobile apps, and they typically match the visual style and tone of the platform. Native ads often include sponsored articles, promoted posts, recommended content, or in-feed ads.
By integrating naturally into the user experience, native ads aim to enhance user engagement and minimize ad fatigue, ultimately increasing their effectiveness in capturing the audience’s attention and driving desired actions.
These categories are the primary types of paid ads utilized by businesses across various digital channels to reach and engage their target audiences.

Having a clear understanding of the financial impact of your paid ad campaigns is crucial for building trust and securing a bigger budget. Before delving into the specifics of structuring Google AdWords and Meta campaigns, let’s discuss the key metrics you should be tracking
Understanding your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is essential for evaluating the effectiveness and profitability of your paid campaigns. Here’s how you can calculate CAC for specific paid campaigns:
CAC = Total Advertising Spend / Number of Customers Acquired
For example, if you spent a total of $5,000 on your ad campaign and acquired 100 customers, your CAC for this campaign would be $50.
Assessing whether this CAC is too high depends on various factors, including the revenue generated by each customer. While $50 might be considered low by tech company standards, it’s crucial to compare your CAC to the lifetime value (LTV) of your customers to determine overall profitability.
Analyzing your CAC alongside metrics like LTV, return on ad spend (ROAS), and average order value (AOV) provides a comprehensive view of your campaign’s performance and helps you make informed decisions about budget allocation and optimization strategies.
Calculating the Customer Acquisition Cost to Lifetime Value (CAC:LTV) ratio provides valuable insights into the long-term profitability of your ad campaigns. Here’s how to calculate and interpret this ratio:
CAC:LTV Ratio = Lifetime Value (LTV) / Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
For example, if your CAC is $50 and your LTV is $400, dividing both numbers by $50 would give you a CAC:LTV ratio of 1:8.
Interpreting the ratio:
However, simply having an LTV higher than your CAC doesn’t guarantee campaign success. It’s crucial to compare your CAC:LTV ratio to a baseline that aligns with your business goals and industry standards. Setting a meaningful benchmark allows you to assess whether your campaigns are delivering the desired return on investment and driving sustainable growth for your business.
Calculating the payback period is crucial for understanding the financial efficiency and growth trajectory of your paid advertising efforts. Here’s how to calculate the payback period for your paid campaigns:
Keep a record of the revenue generated by customers who purchased your product or service after interacting with your paid ads. This revenue should be tracked over multiple quarters to account for variations in purchasing behavior and to capture the full impact of your advertising efforts.
Calculate the total revenue generated by customers acquired through paid ads and compare it to the total cost of your advertising campaigns over the same period. This includes ad spend, creative production costs, and any other associated expenses.
The payback period is the length of time it takes for the revenue generated by customers acquired through paid ads to cover the total cost of the advertising campaigns. Divide the total campaign cost by the revenue generated from paid ad-acquired customers to determine the payback period.
Payback Period = Total Campaign Cost / Revenue from Paid Ad-Acquired Customers
Analyzing the payback period helps you assess the efficiency of your advertising investments and understand how long it takes to recoup the cost of acquiring a customer through paid channels. A shorter payback period indicates faster capital efficiency and a quicker return on investment, whereas a longer payback period may suggest the need for optimization or adjustment in your advertising strategy.
Monitoring changes in the payback period over time can also provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of your ad creative and overall campaign performance. If payback periods are increasing, it may signal the need to refresh your ad creative or explore new targeting strategies to maintain or improve campaign efficiency.
Certainly! Let’s dive deeper into each step of starting with paid advertising:
Defining clear and specific goals is crucial for guiding your paid advertising strategy. Whether it’s raising awareness for a new product or driving online sales, your goals should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For instance, if your objective is to increase brand awareness, you might aim to achieve a certain number of impressions or clicks within a specific timeframe. If your goal is sales, you might focus on metrics like conversion rate and return on ad spend (ROAS).
Knowing your audience inside out is essential for crafting targeted and compelling ads. Conduct thorough market research to gather data on your target market’s demographics, interests, behaviors, and pain points. Creating detailed buyer personas can help you visualize and empathize with your ideal customers, enabling you to tailor your messaging and creative content to resonate with their needs and preferences effectively.
Choosing the most suitable advertising platforms involves considering factors such as audience demographics, competitor activity, platform features, and your own expertise. Analyze where your target audience spends their time online and explore platforms that align with your campaign goals. Whether it’s search engines like Google Ads, social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram, or specialized networks like LinkedIn for B2B targeting, select platforms that offer robust targeting options, analytics, and support for your advertising objectives.
Crafting compelling ad copy and creative elements is essential for capturing your audience’s attention and driving engagement. Use clear, concise language that resonates with your target audience and communicates your value proposition effectively. Incorporate persuasive calls to action (CTAs) to encourage users to take the desired action, whether it’s making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or visiting your website. Ensure consistency between your ad messaging and landing page content to provide a seamless user experience and maximize conversions.
Determining your advertising budget involves balancing your campaign objectives with available resources. Whether you have a fixed budget or are aiming for a specific return on investment (ROI), allocate your budget strategically to maximize campaign effectiveness. Choose a bidding strategy that aligns with your goals, whether it’s maximizing conversions, clicks, or impressions. Consider factors such as competition, audience targeting, and ad placement when setting bids to optimize your campaign performance within your budget constraints.
Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential for ensuring the success of your paid advertising campaigns. Use analytics tools provided by advertising platforms to track key performance metrics such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost per acquisition (CPA). Identify underperforming ads or targeting strategies and make data-driven adjustments to improve results. Conduct A/B testing experiments to compare different ad creatives, targeting options, or bidding strategies and optimize your campaigns based on actionable insights.
Evaluating the return on investment (ROI) and overall performance of your paid advertising campaigns is critical for assessing their effectiveness and informing future strategies. Calculate ROI by comparing the revenue generated from your campaigns to the total advertising costs incurred. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as ROAS, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and lifetime value (LTV) to gauge the overall impact of your advertising efforts on business growth. Use these insights to refine your strategies, reallocate budget towards high-performing campaigns, and drive continuous improvement in your paid advertising initiatives.
By following these steps and adopting a data-driven approach, you can launch and manage successful paid advertising campaigns that drive meaningful results for your business.
Paid advertising allows you to connect with your audience swiftly, driving leads and boosting revenue even with limited budgets.
To launch your first campaign, pick a platform that suits your business objectives and follow the steps outlined earlier. Practice is key to mastering paid ads. However, if you want to ensure that best practices are followed to launch your campaign, you can book a strategy call with us or let our experts launch your campaigns right.
From analyzing your digital presence, and go-to strategy to uncovering new opportunities to grow your business, from identifying new opportunities to get more clients to scaling your business by leveraging paid ads and more, We can guide you. Book a free 30 minute strategy call if you need help with your marketing
638 Independence Parkway, Suite 240, Chesapeake, Virginia, USA – 23320
3 Eurospace, 4th Floor, Jyothi Imperial, Janardana Hills, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, Telangana, India – 500032
Mileta Sorokovska, Moosstrasse 19,
6003 Luzern, Switzerland
Copyright © 2024 by StartupWize